Learn More
C190 In Action
Ratification
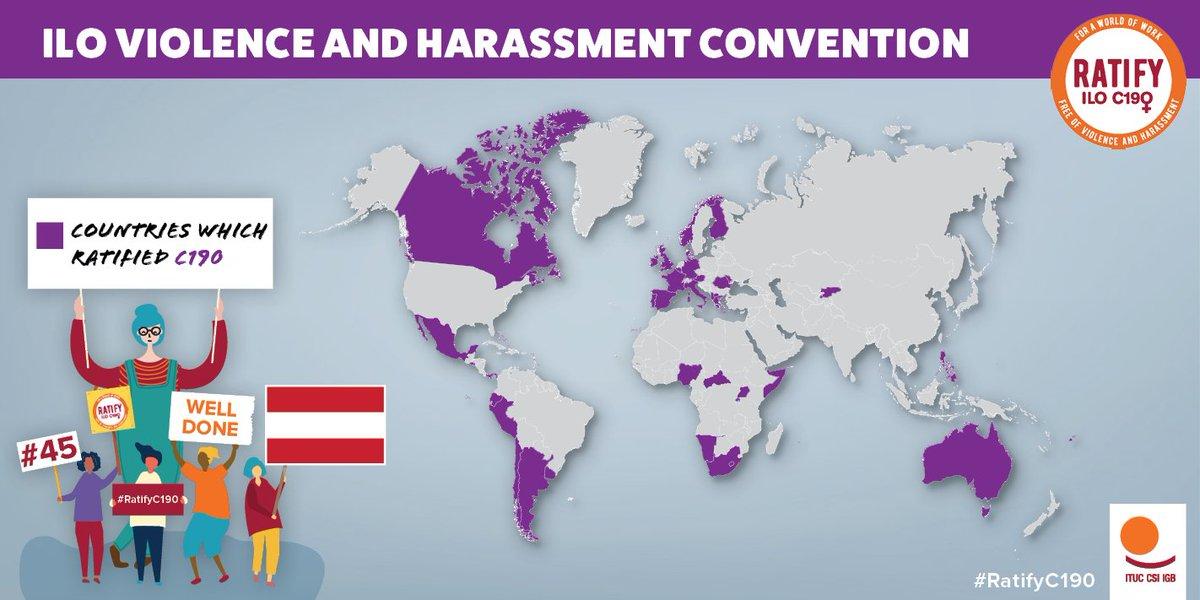
Due to the legally binding nature of C190, when a country ratifies it, it is bound to put in place laws, policies and regulations that address violence and harassment in the world. As of November 2024, 45 countries have ratified C190.
Ratifying countries pledge to apply the convention in national law and practice, and to report on its application to the ILO regularly. Since its adoption, civil society organizations (CSOs), trade unions and other stakeholders have played key roles in leading advocacy campaigns for C190 to be ratified by countries. Check out the promising practices to learn more.
Implementation with ratification
Implementation with ratification includes efforts by governments, civil society organizations (CSOs), trade unions or other stakeholders to implement new policies/laws and/or alter existing policies/laws in line with ILO Convention 190 (C190) and Recommendation 206 (R206) in a ratified country.
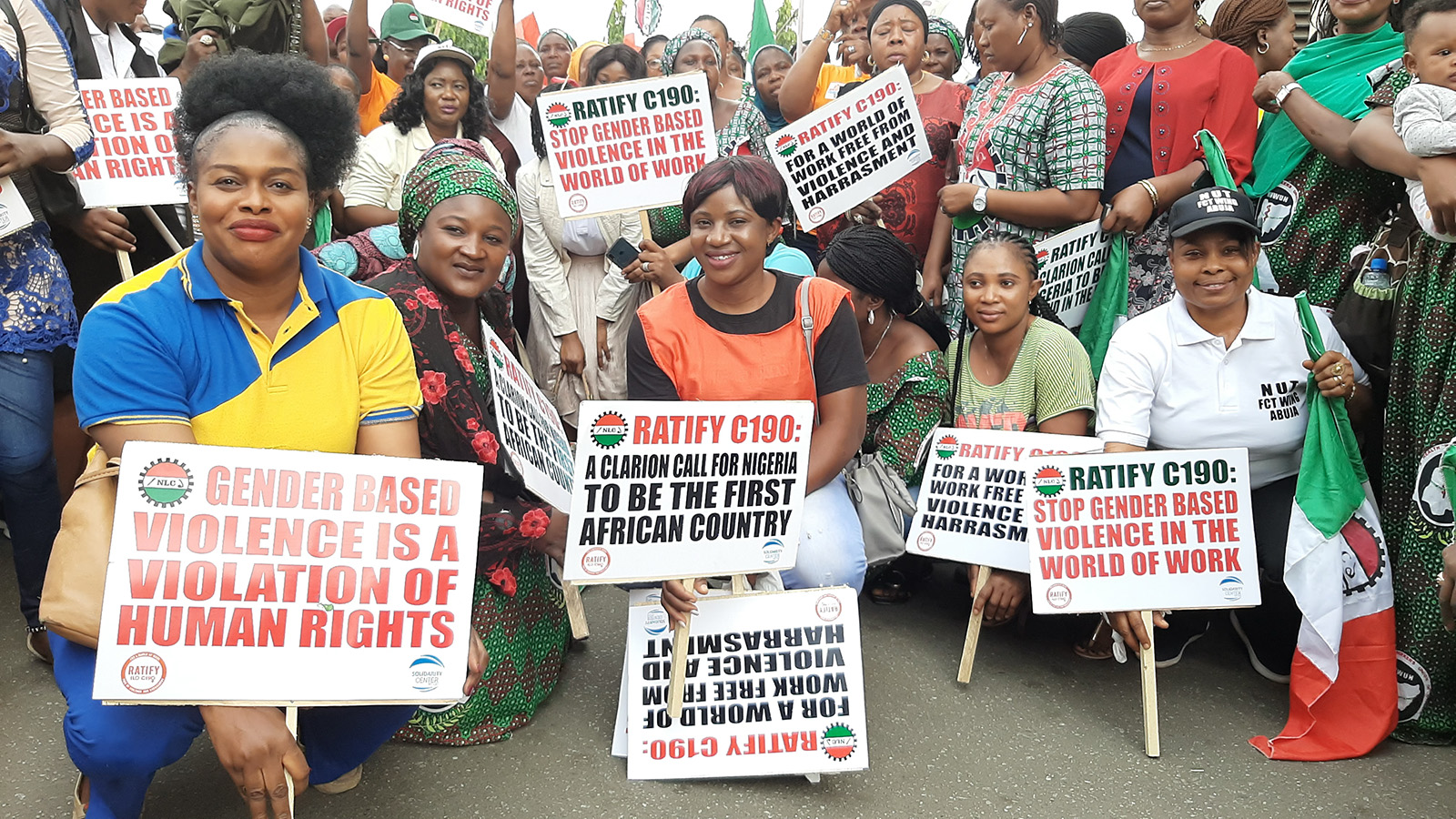

Nigeria Labor Congress celebrates IWD & calls for C190 ratification [Solidarity Center via Nkechi Odinukwe]
Integration without ratification
Integration without ratification includes workplace policies, Collective Bargaining Agreements (CBAs), Enforceable Brand Agreements (EBAs), Global Framework Agreements (GFAs), or other efforts to integrate provisions of ILO Convention 190 (C190) and Recommendation 206 (R206) in contexts where ratification is difficult or pending.
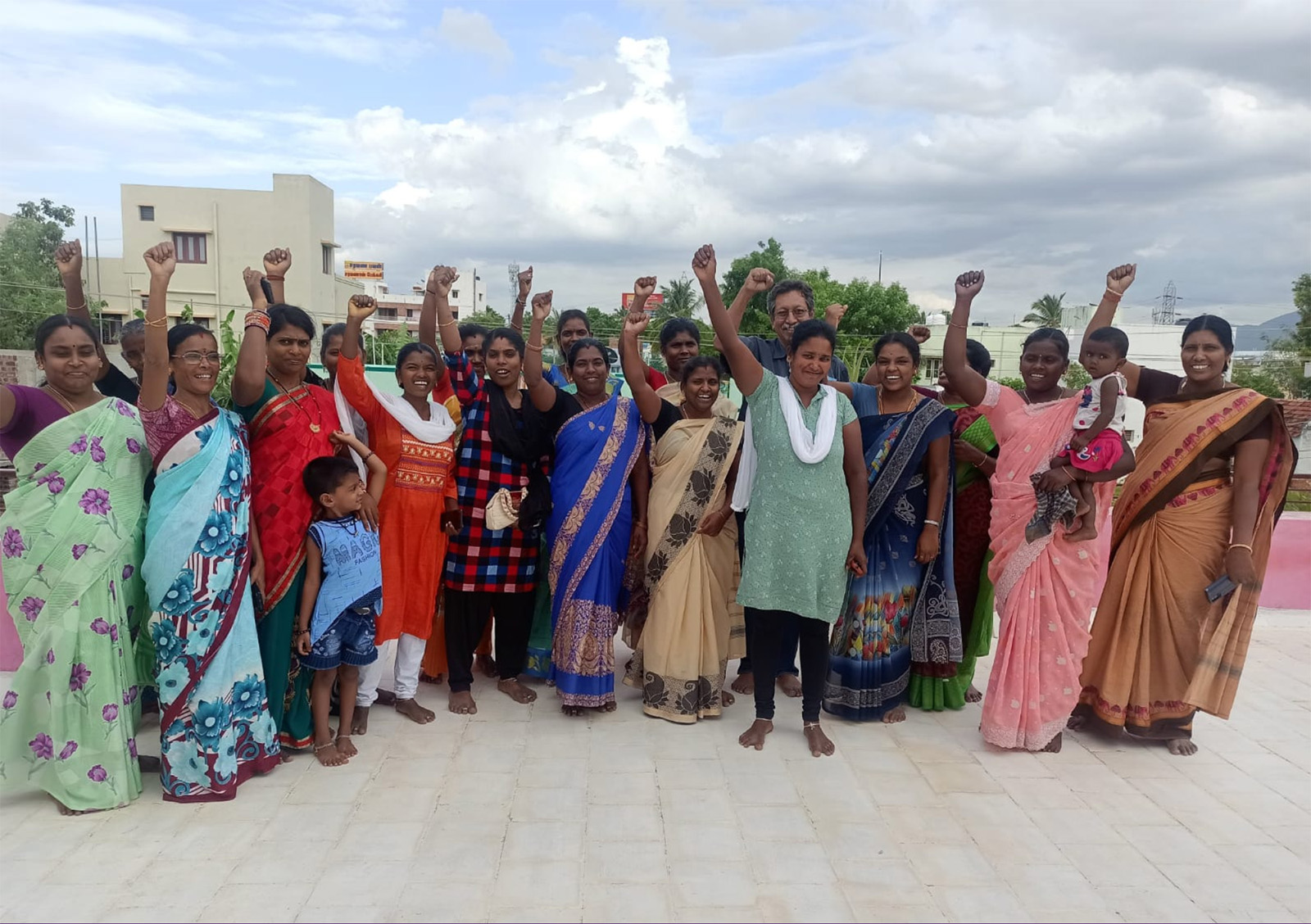

TTCU members celebrate the signing of the Dindigul Agreement [Asia Floor Wage Alliance]